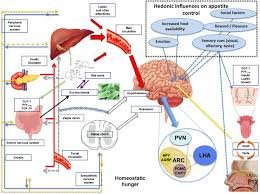
Weight loss can be a complex and challenging process, often influenced by factors beyond diet and exercise. One of the most important but sometimes overlooked aspects of weight management is endocrine health. Your endocrine system, which is made up of glands that produce hormones, plays a key role in regulating metabolism, fat storage, and hunger. When there are imbalances in these hormones, it can make losing weight or maintaining a healthy weight much more difficult.
In this article, we will explore how the endocrine system affects weight loss, the key hormones involved, and the ways to address hormone imbalances to support weight management.
What is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system is a network of glands that release hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones serve as messengers, regulating many of the body’s vital functions, including metabolism, growth, mood, and reproduction. The primary endocrine glands include:
- Hypothalamus (regulates hunger, thirst, body temperature, etc.)
- Pituitary Gland (controls other endocrine glands and growth)
- Thyroid Gland (regulates metabolism)
- Adrenal Glands (manage stress response and metabolism)
- Pancreas (produces insulin to regulate blood sugar levels)
- Gonads (Ovaries and Testes) (affect reproductive hormones and metabolic processes)
When the endocrine system is functioning properly, the body maintains a balance of hormones that helps regulate energy use, fat storage, and appetite. However, when there are hormonal imbalances, it can make weight loss more difficult, leading to weight gain or an inability to lose weight, even with proper diet and exercise.
Key Hormones That Affect Weight Loss
Several hormones play a significant role in weight management. Understanding how these hormones affect the body can help you identify if a hormonal imbalance may be affecting your ability to lose weight.
- Insulin:
- Role in Weight Loss: Insulin is produced by the pancreas and helps regulate blood sugar levels. It also signals the body to store excess energy in the form of fat. High levels of insulin, often caused by insulin resistance (a precursor to type 2 diabetes), can promote fat storage, especially in the abdominal area.
- Impact on Weight Loss: When insulin levels are high, it becomes more difficult for the body to burn fat for energy. Insulin resistance is a common cause of weight gain and may require lifestyle changes, medications, or other interventions to correct.
- Leptin:
- Role in Weight Loss: Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells that helps regulate energy balance by signaling the brain to reduce hunger and increase energy expenditure when fat stores are sufficient.
- Impact on Weight Loss: Leptin resistance can occur when the body no longer responds to leptin signals properly, leading to an increase in hunger and a decrease in energy expenditure. This makes it harder to lose weight, even when calorie intake is reduced.
- Ghrelin:
- Role in Weight Loss: Ghrelin is often referred to as the “hunger hormone.” It is produced in the stomach and signals the brain when it’s time to eat. Ghrelin levels rise before meals and decrease after eating.
- Impact on Weight Loss: High levels of ghrelin can lead to increased hunger, making it difficult to stick to a calorie-restricted diet. Managing ghrelin levels is essential for controlling hunger and promoting weight loss.
- Cortisol:
- Role in Weight Loss: Cortisol is the hormone released by the adrenal glands in response to stress. It plays a role in metabolism by increasing the breakdown of fat and protein for energy. However, chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels.
- Impact on Weight Loss: Elevated cortisol levels over time can lead to fat accumulation, particularly in the abdominal area. Chronic stress and poor sleep can thus hinder weight loss efforts. Reducing stress and improving sleep quality are key factors in regulating cortisol levels and promoting weight loss.
- Thyroid Hormones (T3 and T4):
- Role in Weight Loss: The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism. The most important thyroid hormones for metabolism are T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine).
- Impact on Weight Loss: Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can result in slower metabolism, fatigue, and weight gain. If the thyroid isn’t producing enough hormones, it can be difficult to lose weight or even maintain a healthy weight.
- Estrogen:
- Role in Weight Loss: Estrogen, primarily a female hormone, influences fat distribution and metabolism. It also affects the way the body stores fat, particularly during different stages of life (such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause).
- Impact on Weight Loss: During menopause, a decrease in estrogen levels can lead to weight gain, especially around the abdomen. Additionally, estrogen imbalance, whether too high or too low, can influence appetite and fat storage.
How to Address Endocrine Imbalances for Weight Loss
If you suspect that hormonal imbalances are affecting your weight loss efforts, the first step is to consult with a healthcare professional. A doctor or endocrinologist can perform blood tests and other assessments to diagnose any underlying hormonal issues. Once an imbalance is identified, treatment can be tailored to address the specific problem.
Here are some strategies to help manage hormone levels and support weight loss:
- Manage Insulin Levels:
- Diet: Reducing your intake of processed carbohydrates and sugar can help improve insulin sensitivity. Focus on eating whole foods, high-fiber vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, especially strength training, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce fat storage.
- Medications: In some cases, medications like metformin may be prescribed to help control insulin resistance and manage blood sugar levels.
- Regulate Leptin and Ghrelin:
- Eat Enough Protein: Protein-rich foods can help regulate hunger and increase satiety, reducing the effects of ghrelin.
- Improve Sleep: Poor sleep can negatively affect leptin and ghrelin levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support hormonal balance.
- Intermittent Fasting: Some research suggests that intermittent fasting may help regulate leptin and ghrelin levels, potentially supporting weight loss efforts.
- Control Cortisol Levels:
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time outdoors.
- Quality Sleep: Ensure that you’re getting enough rest. Chronic sleep deprivation can elevate cortisol levels, making it harder to lose weight.
- Balanced Diet: Include stress-busting foods such as fatty fish (rich in omega-3s), nuts, and whole grains to support cortisol regulation.
- Support Thyroid Function:
- Nutrient Support: Ensure you’re getting enough iodine, selenium, and zinc, as these nutrients are essential for healthy thyroid function.
- Thyroid Hormone Replacement: If hypothyroidism is diagnosed, thyroid hormone replacement therapy (such as levothyroxine) may be necessary to normalize hormone levels and restore metabolism.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy for Estrogen:
- Hormone Therapy: For women experiencing menopause-related weight gain due to estrogen decline, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may help restore hormonal balance and reduce fat storage.
- Phytoestrogens: Some plant-based foods contain phytoestrogens (like soy products), which may help balance estrogen levels naturally. However, it’s important to discuss this with a healthcare provider.
- Regular Physical Activity:
- Exercise can help regulate hormone levels by improving insulin sensitivity, balancing cortisol, and supporting thyroid function. Both aerobic and strength training exercises are important for maintaining hormonal balance and supporting weight loss.
Conclusion: The Connection Between Endocrine Health and Weight Loss
Hormonal imbalances can significantly impact weight loss, making it difficult to shed pounds or maintain a healthy weight. Understanding how hormones like insulin, leptin, ghrelin, cortisol, thyroid hormones, and estrogen affect your metabolism and fat storage can help you take targeted steps to address these issues. By managing stress, improving sleep, making dietary adjustments, and seeking medical treatment when necessary, you can optimize your endocrine health and support your weight loss goals.